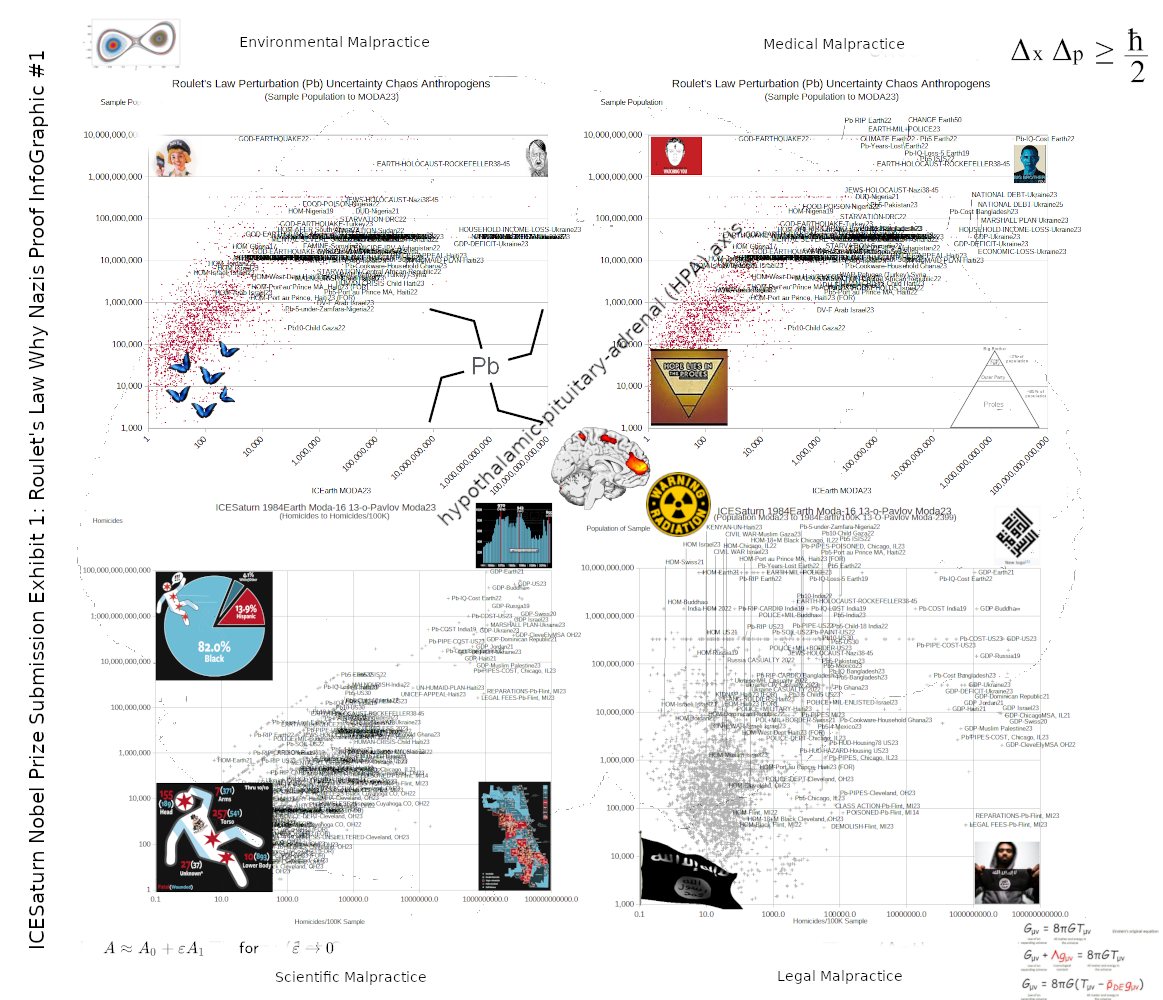
 Roulet's Law is Perturbation (1st order Pb) X Uncertainty = Chaos X Relativity
Roulet's Law is Perturbation (1st order Pb) X Uncertainty = Chaos X Relativity
In mathematics and applied mathematics, perturbation theory comprises methods for finding an approximate solution to a problem, by starting from the exact solution of a related, simpler problem.
An approximate "perturbative solution" is obtained by truncating the series, often by keeping only the first two terms, expressing the final solution as a sum of the initial (exact) solution and the "first-order" perturbative correction
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perturbation_theory
Formulated by the German physicist and Nobel laureate Werner Heisenberg in 1927, the uncertainty principle states that we cannot know both the position and speed of a particle, such as a photon or electron, with perfect accuracy; the more we nail down the particle's position, the less we know about its speed and vice versa.
In other words, if we could shrink a tortoise down to the size of an electron, we would only be able to precisely calculate its speed or its location, not both at the same time.
Though the Heisenberg uncertainty principle is famously known in quantum physics, a similar uncertainty principle also applies to problems in pure math and classical physics—basically, any object with wave-like properties will be affected by this principle. Quantum objects are special because they all exhibit wave-like properties by the very nature of quantum theory.
The uncertainty principle is a trade-off between two complementary variables, such as position and speed.
The fundamental law comes into play in the quantum world because subatomic particles can behave like waves. A common misconception about the uncertainty principle in quantum physics is that it implies our measurements are uncertain or inaccurate. In fact, uncertainty is an inherent aspect of anything with wave-like behavior.
https://scienceexchange.caltech.edu/topics/quantum-science-explained/uncertainty-principle
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of scientific study and branch of mathematics. It focuses on underlying patterns and deterministic laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions. These were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. Chaos theory states that within the apparent randomness of chaotic complex systems, there are underlying patterns, interconnection, constant feedback loops, repetition, self-similarity, fractals and self-organization. The butterfly effect, an underlying principle of chaos, describes how a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state (meaning there is sensitive dependence on initial conditions). A metaphor for this behavior is that a butterfly flapping its wings in Brazil can cause a tornado in Texas.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chaos_theory
AI Overview-
In physics, relativity is a theory that states that space and time are relative, and that all motion is relative to a frame of reference. It also states that the laws of physics are the same everywhere.
